新疆模板网站建设整站优化服务
前面我们讲到了 贪心算法的哈夫曼编码规则,原理图如下:
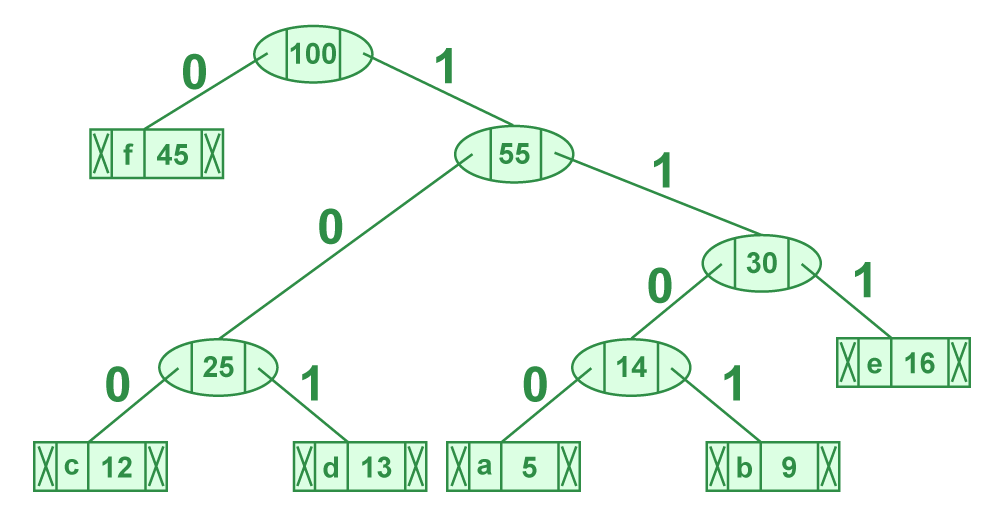
如果我们知道给定的数组已排序(按频率的非递减顺序),我们可以在 O(n) 时间内生成霍夫曼代码。以下是用于排序输入的 O(n) 算法。
1.创建两个空队列。
2.为每个唯一字符创建一个叶节点,并按频率非降序将其入队到第一个队列。最初第二个队列是空的。
3.通过检查两个队列的前端以最小频率使两个节点出队。重复以下步骤两次
1. 如果第二个队列为空,则从第一个队列中出队。
2. 如果第一个队列为空,则从第二个队列中出队。
3. 否则,比较两个队列的前端并将最小值出队。
4.创建一个新的内部节点,其频率等于两个节点频率的总和。将第一个 Dequeued 节点作为其左子节点,将第二个 Dequeued 节点作为右子节点。将此节点排入第二个队列。
5.当队列中有多个节点时,重复步骤#3 和#4。剩下的节点是根节点,树就完成了。
// C++ Program for Efficient Huffman Coding for Sorted input
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;// This constant can be avoided by explicitly
// calculating height of Huffman Tree
#define MAX_TREE_HT 100// A node of huffman tree
class QueueNode {
public:char data;unsigned freq;QueueNode *left, *right;
};// Structure for Queue: collection
// of Huffman Tree nodes (or QueueNodes)
class Queue {
public:int front, rear;int capacity;QueueNode** array;
};// A utility function to create a new Queuenode
QueueNode* newNode(char data, unsigned freq)
{QueueNode* temp = new QueueNode[(sizeof(QueueNode))];temp->left = temp->right = NULL;temp->data = data;temp->freq = freq;return temp;
}// A utility function to create a Queue of given capacity
Queue* createQueue(int capacity)
{Queue* queue = new Queue[(sizeof(Queue))];queue->front = queue->rear = -1;queue->capacity = capacity;queue->array = new QueueNode*[(queue->capacity* sizeof(QueueNode*))];return queue;
}// A utility function to check if size of given queue is 1
int isSizeOne(Queue* queue)
{return queue->front == queue->rear&& queue->front != -1;
}// A utility function to check if given queue is empty
int isEmpty(Queue* queue) { return queue->front == -1; }// A utility function to check if given queue is full
int isFull(Queue* queue)
{return queue->rear == queue->capacity - 1;
}// A utility function to add an item to queue
void enQueue(Queue* queue, QueueNode* item)
{if (isFull(queue))return;queue->array[++queue->rear] = item;if (queue->front == -1)++queue->front;
}// A utility function to remove an item from queue
QueueNode* deQueue(Queue* queue)
{if (isEmpty(queue))return NULL;QueueNode* temp = queue->array[queue->front];if (queue->front== queue->rear) // If there is only one item in queuequeue->front = queue->rear = -1;else++queue->front;return temp;
}// A utility function to get from of queue
QueueNode* getFront(Queue* queue)
{if (isEmpty(queue))return NULL;return queue->array[queue->front];
}/* A function to get minimum item from two queues */
QueueNode* findMin(Queue* firstQueue, Queue* secondQueue)
{// Step 3.a: If first queue is empty, dequeue from// second queueif (isEmpty(firstQueue))return deQueue(secondQueue);// Step 3.b: If second queue is empty, dequeue from// first queueif (isEmpty(secondQueue))return deQueue(firstQueue);// Step 3.c: Else, compare the front of two queues and// dequeue minimumif (getFront(firstQueue)->freq< getFront(secondQueue)->freq)return deQueue(firstQueue);return deQueue(secondQueue);
}// Utility function to check if this node is leaf
int isLeaf(QueueNode* root)
{return !(root->left) && !(root->right);
}// A utility function to print an array of size n
void printArr(int arr[], int n)
{int i;for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)cout << arr[i];cout << endl;
}// The main function that builds Huffman tree
QueueNode* buildHuffmanTree(char data[], int freq[],int size)
{QueueNode *left, *right, *top;// Step 1: Create two empty queuesQueue* firstQueue = createQueue(size);Queue* secondQueue = createQueue(size);// Step 2:Create a leaf node for each unique character// and Enqueue it to the first queue in non-decreasing// order of frequency. Initially second queue is emptyfor (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)enQueue(firstQueue, newNode(data[i], freq[i]));// Run while Queues contain more than one node. Finally,// first queue will be empty and second queue will// contain only one nodewhile (!(isEmpty(firstQueue) && isSizeOne(secondQueue))) {// Step 3: Dequeue two nodes with the minimum// frequency by examining the front of both queuesleft = findMin(firstQueue, secondQueue);right = findMin(firstQueue, secondQueue);// Step 4: Create a new internal node with frequency// equal to the sum of the two nodes frequencies.// Enqueue this node to second queue.top = newNode('$', left->freq + right->freq);top->left = left;top->right = right;enQueue(secondQueue, top);}return deQueue(secondQueue);
}// Prints huffman codes from the root of Huffman Tree. It
// uses arr[] to store codes
void printCodes(QueueNode* root, int arr[], int top)
{// Assign 0 to left edge and recurif (root->left) {arr[top] = 0;printCodes(root->left, arr, top + 1);}// Assign 1 to right edge and recurif (root->right) {arr[top] = 1;printCodes(root->right, arr, top + 1);}// If this is a leaf node, then it contains one of the// input characters, print the character and its code// from arr[]if (isLeaf(root)) {cout << root->data << ": ";printArr(arr, top);}
}// The main function that builds a Huffman Tree and print
// codes by traversing the built Huffman Tree
void HuffmanCodes(char data[], int freq[], int size)
{// Construct Huffman TreeQueueNode* root = buildHuffmanTree(data, freq, size);// Print Huffman codes using the Huffman tree built// aboveint arr[MAX_TREE_HT], top = 0;printCodes(root, arr, top);
}// Driver code
int main()
{char arr[] = { 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f' };int freq[] = { 5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45 };int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);HuffmanCodes(arr, freq, size);return 0;
}// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
Output:
f: 0 c: 100 d: 101 a: 1100 b: 1101 e: 111
QueueNode结构题代表哈夫曼的树结构
Queue的结构:集合霍夫曼树节点(或QueueNodes)
函数newNode:一个用于创建新Queuenode的实用函数
函数deQueue:从队列中删除项目的实用函数
函数HuffmanCodes:构建霍夫曼树并打印的主要函数代码通过遍历构建的霍夫曼树
函数printCodes:从霍夫曼树的根部打印霍夫曼代码。它使用arr[]存储代码
函数buildHuffmanTree:构建霍夫曼树的主要功能
- 步骤1:创建两个空队列
- 步骤2:为每个唯一的字符创建一个叶节点和在非递减队列中将它排到第一个队列频率的顺序。最初第二个队列为空。当队列包含多个节点时运行。最后,第一个队列为空,第二个队列为空只包含一个节点
- 步骤3:从队列中取出最小的两个节点通过检查两个队列的前面
- 步骤4:创建一个新的内部节点等于两个节点频率的和。将该节点加入第二个队列。
java代码实现如下:
// JavaScript program for the above approach// Class for the nodes of the Huffman tree
class QueueNode {
constructor(data = null, freq = null, left = null, right = null) {this.data = data;this.freq = freq;this.left = left;this.right = right;
}// Function to check if the following// node is a leaf node
isLeaf() {return (this.left == null && this.right == null);
}
}// Class for the two Queues
class Queue {
constructor() {this.queue = [];
}// Function for checking if the
// queue has only 1 node
isSizeOne() {return this.queue.length == 1;
}// Function for checking if
// the queue is empty
isEmpty() {return this.queue.length == 0;
}// Function to add item to the queue
enqueue(x) {this.queue.push(x);
}// Function to remove item from the queue
dequeue() {return this.queue.shift();
}
}// Function to get minimum item from two queues
function findMin(firstQueue, secondQueue) {// Step 3.1: If second queue is empty,
// dequeue from first queue
if (secondQueue.isEmpty()) {return firstQueue.dequeue();
}// Step 3.2: If first queue is empty,
// dequeue from second queue
if (firstQueue.isEmpty()) {return secondQueue.dequeue();
}// Step 3.3: Else, compare the front of
// two queues and dequeue minimum
if (firstQueue.queue[0].freq < secondQueue.queue[0].freq) {return firstQueue.dequeue();
}return secondQueue.dequeue();
}// The main function that builds Huffman tree
function buildHuffmanTree(data, freq, size) {
// Step 1: Create two empty queues
let firstQueue = new Queue();
let secondQueue = new Queue();// Step 2: Create a leaf node for each unique
// character and Enqueue it to the first queue
// in non-decreasing order of frequency.
// Initially second queue is empty.
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {firstQueue.enqueue(new QueueNode(data[i], freq[i]));
}// Run while Queues contain more than one node.
// Finally, first queue will be empty and
// second queue will contain only one node
while (!(firstQueue.isEmpty() && secondQueue.isSizeOne())) {// Step 3: Dequeue two nodes with the minimum// frequency by examining the front of both queueslet left = findMin(firstQueue, secondQueue);let right = findMin(firstQueue, secondQueue);// Step 4: Create a new internal node with// frequency equal to the sum of the two// nodes frequencies. Enqueue this node// to second queue.let top = new QueueNode("$", left.freq + right.freq, left, right);secondQueue.enqueue(top);
}return secondQueue.dequeue();
}// Prints huffman codes from the root of
// Huffman tree. It uses arr[] to store codes
function printCodes(root, arr) {// Assign 0 to left edge and recur
if (root.left) {arr.push(0);printCodes(root.left, arr);arr.pop();
}// Assign 1 to right edge and recur
if (root.right) {arr.push(1);printCodes(root.right, arr);arr.pop();
}// If this is a leaf node, then it contains
// one of the input characters, print the
// character and its code from arr[]
if (root.isLeaf()) {let output = root.data + ": ";for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {output += arr[i];}console.log(output);
}
}// The main function that builds a Huffman
// tree and print codes by traversing the
// built Huffman tree
function HuffmanCodes(data, freq, size) {// Construct Huffman Tree
let root = buildHuffmanTree(data, freq, size);// Print Huffman codes using the Huffman
// tree built above
let arr = [];
printCodes(root, arr);
}// Driver code
let arr = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"];
let freq = [5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45];
let size = arr.length;
HuffmanCodes(arr, freq, size);// This code is contributed by Prince Kumar
时间复杂度: O(n)
如果输入没有排序,需要先排序后才能被上面的算法处理。可以使用在 Theta(nlogn) 中运行的堆排序或合并排序来完成排序。因此,对于未排序的输入,整体时间复杂度变为 O(nlogn)。
辅助空间: O(n)
