中山网站建设seo135谷歌chrome安卓版
目录
1.同步的接口
2.多线程但是按顺序来执行
3.生产消费模型
4.使用互斥加同步实现生产消费模型 (采用环形队列)
同步:在保证数据安全的前提下,让线程能够按照某种特定的顺序访问临界资源,从而有效避免饥饿问题
1.同步的接口
pthread_cond_t 是条件变量;
2.多线程但是按顺序来执行
- 保证了每个线程都被执行,没有饥饿问题
#include<iostream>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
using namespace std;pthread_cond_t cond;//条件变量
pthread_mutex_t mtx;
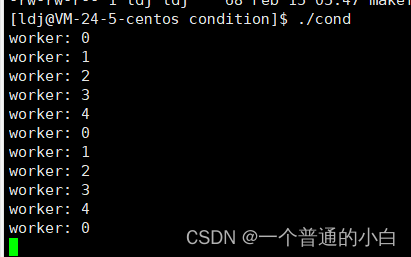
void* Work(void* args)
{int num=*((int*)args);delete (int*)args;while(1){pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mtx);cout<<"worker: "<<num<<endl;}
}
void* Control(void* args)
{while(1){pthread_cond_signal(&cond);sleep(1);}
}
int main()
{//初始化条件变量和互斥锁pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);pthread_mutex_init(&mtx,NULL);pthread_t master;pthread_t worker[5];for(int i=0;i<5;i++){//5个轻量级进程int* tmp=new int(i);pthread_create(worker+i,NULL,Work,(void*)tmp);}pthread_create(&master,NULL,Control,NULL);//使用同步管理另外5个轻量级进程按特定顺序执行//等待轻量级进程for(int i=0;i<5;i++){pthread_join(worker[i],NULL);}//释放条件变量和互斥锁pthread_join(master,NULL);pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);return 0;
}执行结果:
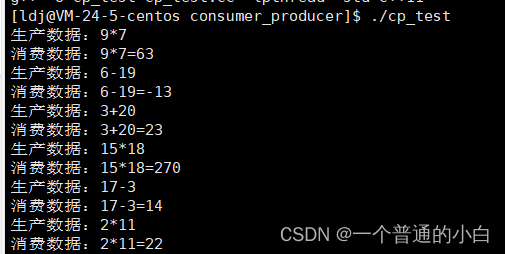
3.生产消费模型

4.使用互斥加同步实现生产消费模型 (采用环形队列)
条件变量判断应采用while而不是if,线程被挂起其他,线程可能会修改临界资源,pthread_cond_signal唤醒线程可能条件不再满足;
if(判断条件)//不完全正确的{pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,&_mtx);}
while(判断条件)//正确{pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,&_mtx);}BlockQueue.hpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<pthread.h>#define CAPACITY 10namespace ds_blockqueue{template<class T>class BlockQueue{private:std::queue<T> bq;//先入先出队列int cap;//容量//两个条件变量和一个互斥锁pthread_cond_t pc;pthread_cond_t cc;pthread_mutex_t mtx;public:BlockQueue():cap(CAPACITY){pthread_cond_init(&pc,nullptr);pthread_cond_init(&cc,nullptr);pthread_mutex_init(&mtx,nullptr);}~BlockQueue(){pthread_cond_destroy(&pc);pthread_cond_destroy(&cc);pthread_mutex_destroy(&mtx);}private:void WaitProducer(){pthread_cond_wait(&pc,&mtx);}void WaitConsumer(){pthread_cond_wait(&cc,&mtx);}void WakeupProducer(){pthread_cond_signal(&pc);}void WakeupConsumer(){pthread_cond_signal(&cc);}void Lock(){pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx);}void Unlock(){pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx);}private:bool IsFull(){return bq.size()==cap;}bool IsEmpty(){return bq.size()==0;}public://当满时生产者需要等待消费者消费//当空时消费者需要等待生产者生产void Push(const T& in){Lock();while(IsFull())//被挂起如果其他轻量级进程修改临界资源,使用if判断这个条件条件不一定是满足的使用while免得伪唤醒{WaitProducer();}bq.push(in);//生成一个就可以消费了//if(bq.size()>=cap/2)WakeupConsumer(); Unlock();}void Pop(T* out){Lock();while(IsEmpty())//被挂起如果其他轻量级进程修改临界资源,使用if判断这个条件条件不一定是满足的使用while免得伪唤醒{WaitConsumer();}*out=bq.front();bq.pop();//消费一个就可以生产了//if(bq.size()<=cap/2)WakeupProducer();Unlock();}};
}cp_test.cc
#include "BlockQueue.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
#include<unistd.h>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<time.h>
using namespace ds_blockqueue;
using namespace ds_task;const char* op="+-*/";
void* Consumer(void* args)
{BlockQueue<Task>* bq=(BlockQueue<Task>*)args;while(true){Task t;int data=0;bq->Pop(&t);std::cout<<"消费数据:";t();sleep(1);}
}
void* Producer(void* args)
{BlockQueue<Task>* bq=(BlockQueue<Task>*)args;while(true){int x=rand()%20+1;int y=rand()%20+1;char tmp=op[rand()%4];Task t(x,y,tmp);// //制造数据// int data=rand()%10+1;//std::cout<<"生产数据:"<<data<<std::endl;std::cout<<"生产数据:"<<x<<tmp<<y<<std::endl;bq->Push(t);sleep(2);}
}
int main()
{srand((long long)time(nullptr));BlockQueue<Task>* bq=new BlockQueue<Task>;//创建阻塞队列pthread_t pid1;pthread_t pid2;//创建消费者和生产者pthread_create(&pid1,nullptr,Consumer,(void*)bq);pthread_create(&pid2,nullptr,Producer,(void*)bq);pthread_join(pid1,nullptr);pthread_join(pid2,nullptr);return 0;
}Task.hpp:处理数据
#include<iostream>namespace ds_task{class Task{private:int _x;int _y;char _op;public:Task(){}Task(const int& x,const int& y,const char& op) :_x(x),_y(y),_op(op) {}~Task(){}void operator()(){int tatol=0;switch(_op){case '+':tatol=_x+_y;break;case '-':tatol=_x-_y;break;case '*':tatol=_x*_y;break;case '/':tatol=_x/_y;break;default:break;}std::cout<<_x<<_op<<_y<<"="<<tatol<<std::endl;}};
}执行结果: