政府集约化网站群建设方案企业品牌营销推广
文章目录
- 一、引入
- 二、状态模式
- 2.1 Intent 意图
- 2.2 Applicability 适用性
- 2.3 类图
- 2.4 Collaborations 合作
- 2.5 Implementation 实现
- 2.5 状态模式与策略模式的对比
- 2.5 状态模式实例:糖果机
- 2.6 状态模式实例:自行车升降档
一、引入
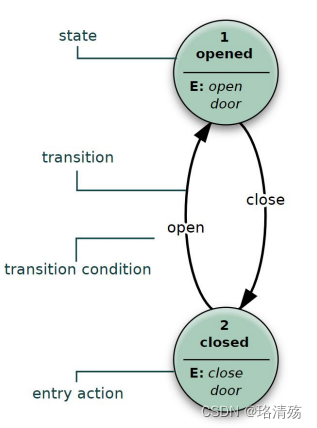
- State Diagram 状态图:
A state diagram is a type of diagram used in computer science and related fields to describe the behavior of systems.
状态图是在计算机科学和相关领域中用于描述系统行为的一种图.
Parts of UML
- 糖果机问题
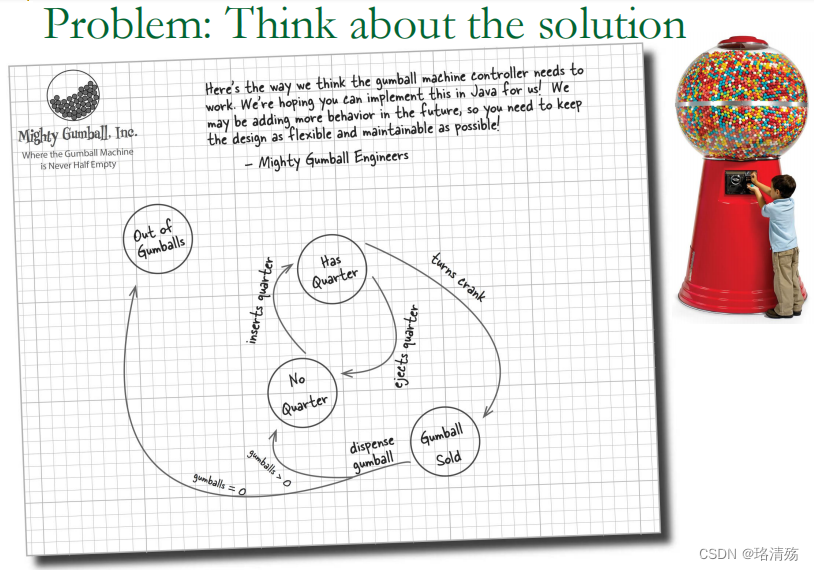
- 状态汇总:No Quarter(无 25 美分)、Has Quarter(有 25 美分)、Gumball Sold(糖果售出)、Out Of Gumballs(糖果售罄)attribute value
- 行为汇总:insert quarter(投币)、ejects quarter(吐币)、turns crank(转动曲柄)、dispense(出糖果,For machine)method
package net.dp.state.gumball;public class GumballMachine {final static int SOLD_OUT = 0;final static int NO_QUARTER = 1;final static int HAS_QUARTER = 2;final static int SOLD = 3;int state = SOLD_OUT;int count = 0;public GumballMachine(int count) {this.count = count;if (count > 0) {state = NO_QUARTER;}}public void insertQuarter() {if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {System.out.println("You can't insert another quarter");} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {state = HAS_QUARTER;System.out.println("You inserted a quarter");} else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {System.out.println("You can't insert a quarter, the machine is sold out");} else if (state == SOLD) {System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a gumball");}}public void ejectQuarter() {if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {System.out.println("Quarter returned");state = NO_QUARTER;} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {System.out.println("You haven't inserted a quarter");} else if (state == SOLD) {System.out.println("Sorry, you already turned the crank");} else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {System.out.println("You can't eject, you haven't inserted a quarter yet");}}public void turnCrank() {if (state == SOLD) {System.out.println("Turning twice doesn't get you another gumball!");} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {System.out.println("You turned but there's no quarter");} else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {System.out.println("You turned, but there are no gumballs");} else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {System.out.println("You turned...");state = SOLD;dispense();}}public void dispense() {if (state == SOLD) {System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot");count = count - 1;if (count == 0) {System.out.println("Oops, out of gumballs!");state = SOLD_OUT;} else {state = NO_QUARTER;}} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {System.out.println("You need to pay first");} else if (state == SOLD_OUT) {System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");} else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");}}public void refill(int numGumBalls) {this.count = numGumBalls;state = NO_QUARTER;}public String toString() {StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();result.append("\nMighty Gumball, Inc.");result.append("\nJava-enabled Standing Gumball Model #2004\n");result.append("Inventory: " + count + " gumball");if (count != 1) {result.append("s");}result.append("\nMachine is ");if (state == SOLD_OUT) {result.append("sold out");} else if (state == NO_QUARTER) {result.append("waiting for quarter");} else if (state == HAS_QUARTER) {result.append("waiting for turn of crank");} else if (state == SOLD) {result.append("delivering a gumball");}result.append("\n");return result.toString();}
}Terrible implements!
需求变更:
提升销量,10 % 的可能出两个糖果

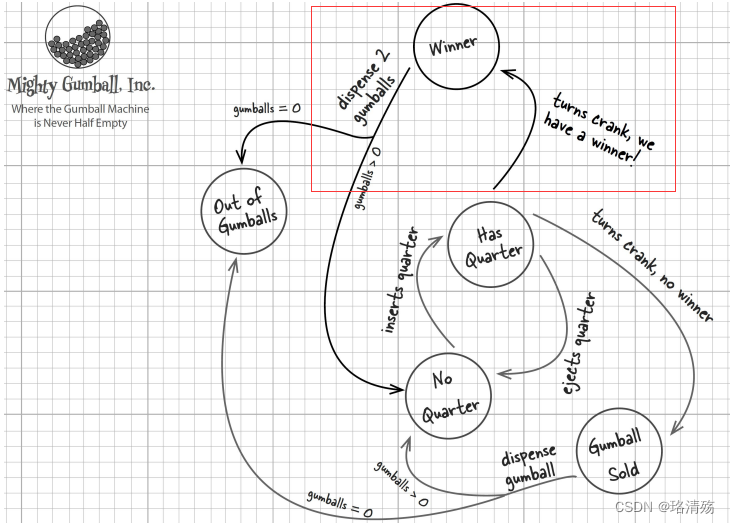
难以维护:

二、状态模式
2.1 Intent 意图
- Allow an object to alter its behavior when its internal state changes. The object will appear to change its class. 状态模式允许一个对象在其内部状态改变的时候改变其行为,这个对象看上去就像改变了它的类一样.
2.2 Applicability 适用性
- An object’s behavior depends on its state, and it must change its behavior at run-time depending on that state. 对象的行为取决于它的状态,它必须根据运行状态改变它的行为.
- Operations have large, multipart conditional statements that depend on the object’s state. 操作有依赖于对象状态的大量的、多部分的条件语句.
2.3 类图
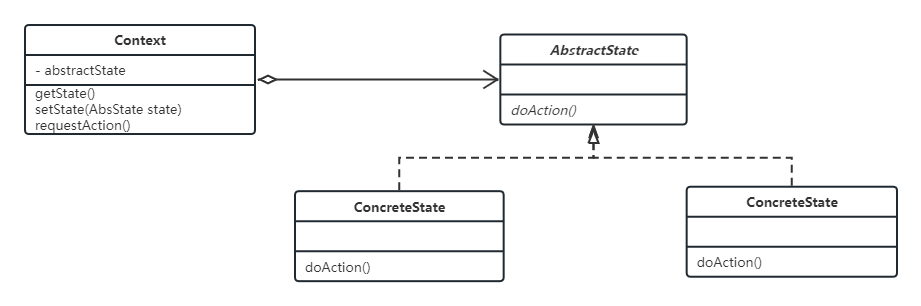
- Context: Defines the interface of interest to clients; maintains an instance of a ConcreteState that defines the current state.
- State: Defines an interface for encapsulating the behavior associated with a particular state of the Context.
- ConcreteState: each implements a behavior associated with a state of the Context.
2.4 Collaborations 合作
- Context delegates state-specific requests to the current ConcreteState object. Context 把状态相关的请求代理到当前的 ConcreteState 对象。
- A context may pass itself as an argument to the State object handling the request. This lets the State object access the context if necessary. context 可以将自身作为参数传递给处理该请求的状态对象,以允许状态对象在必要时访问上下文。
- Context is the primary interface for clients. State objects can be configured to context. Once a context is configured, its clients don’t have to deal with the State objects directly. Context 是 Client 的主要接口,状态对象可以配置到 context,并且一旦配置了状态,Client 就不必直接处理状态对象了。
- Either Context or the ConcreteState can decide which state succeeds another and under what circumstances. Context 或 ConcreateState 均能决定 state 的后继状态是哪个以及在什么条件下(状态的变化如何)
2.5 Implementation 实现
-
Who defines the state transitions? 谁定义状态转换
- The State pattern does not specify which participant defines the criteria for state transitions. 状态模式并不指定哪个参与者(Context、State)定义了状态转换的标准.
- If the criteria are fixed, then they can be implemented entirely in the Context. 如果转换标准是固定的,那么它们就可以完全在 Context 中实现.
- It is generally more flexible and appropriate to let the State subclasses themselves specify their successor state and when to make the transition. 通常,让状态子类本身指定它们的后继状态以及何时进行转换更加灵活和合适.
- It is easy to modify or extend the logic by defining new State subclasses. 易于通过定义新 State 子类修改或扩展逻辑
- A disadvantage is State subclass will have knowledge of at least one other, which introduces implementation dependencies between subclasses. 一个缺点是状态子类至少知道一个其他子类,这就引入了子类之间的实现依赖关系。
-
Creating and destroying State objects. 创建与销毁状态对象
- Lazy: to create State objects only when they are needed and destroy them thereafter. 只在需要状态对象时创建状态对象,并在此之后销毁它们
- When the states that will be entered aren’t known at runtime, and contexts change state infrequently. 当运行时不知道将输入的状态,且上下文 contexts 很少改变状态时.
- Eager: creating them ahead of time and never destroying them. 提前创造出它们,但从不摧毁它们
- When state changes occur rapidly. 状态改变频繁时
- Lazy: to create State objects only when they are needed and destroy them thereafter. 只在需要状态对象时创建状态对象,并在此之后销毁它们
2.5 状态模式与策略模式的对比
- Same:类图基本一致
- Diff
- Strategy: One state with many algorithms
- 一个具有多个算法实现的抽象状态,采用哪个由 Client 决定
- State: many States with different behaviors - 多个 具有不同行为的状态,一个状态对应一个行为
- 采用哪个可以由 Client 决定,且运行过程中状态可以改变,从而行为也得到改变
- Strategy: One state with many algorithms
状态模式与策略模式很相似,状态是将类的"状态"封装了起来,在执行动作时进行自动的转换,从而实现类在不同状态下的同一动作显示出不同结果。
它与策略模式的区别在于,这种转换是"自动","无意识"的。
关于策略模式:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44992559/article/details/115007554
2.5 状态模式实例:糖果机
变更需求实现
- 糖果机:即 Context
public class GumballMachine {State soldOutState;State noQuarterState;State hasQuarterState;State soldState;State winnerState;State state = soldOutState;int count = 0;public GumballMachine(int numberGumballs) {soldOutState = new SoldOutState(this);noQuarterState = new NoQuarterState(this);hasQuarterState = new HasQuarterState(this);soldState = new SoldState(this);winnerState = new WinnerState(this);this.count = numberGumballs;if (numberGumballs > 0) {state = noQuarterState;} }public void insertQuarter() {state.insertQuarter();}public void ejectQuarter() {state.ejectQuarter();}public void turnCrank() {state.turnCrank();state.dispense();}void setState(State state) {this.state = state;}void releaseBall() {System.out.println("A gumball comes rolling out the slot...");if (count != 0) {count = count - 1;}}int getCount() {return count;}void refill(int count) {this.count = count;state = noQuarterState;}public State getState() {return state;}public State getSoldOutState() {return soldOutState;}public State getNoQuarterState() {return noQuarterState;}public State getHasQuarterState() {return hasQuarterState;}public State getSoldState() {return soldState;}public State getWinnerState() {return winnerState;}public String toString() {StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();result.append("\nMighty Gumball, Inc.");result.append("\nJava-enabled Standing Gumball Model #2004");result.append("\nInventory: " + count + " gumball");if (count != 1) {result.append("s");}result.append("\n");result.append("Machine is " + state + "\n");return result.toString();}
}- 糖果机状态接口:抽象状态
public interface State {public void insertQuarter();public void ejectQuarter();public void turnCrank();public void dispense();
}
- 有 25 美分硬币状态
public class HasQuarterState implements State {Random randomWinner = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());GumballMachine gumballMachine;public HasQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;}public void insertQuarter() {System.out.println("You can't insert another quarter");}public void ejectQuarter() {System.out.println("Quarter returned");gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());}public void turnCrank() {System.out.println("You turned...");int winner = randomWinner.nextInt(10);if ((winner == 0) && (gumballMachine.getCount() > 1)) {gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getWinnerState());} else {gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldState());}}public void dispense() {System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");}public String toString() {return "waiting for turn of crank";}
}- 无 25 美分硬币状态
public class NoQuarterState implements State {GumballMachine gumballMachine;public NoQuarterState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;}public void insertQuarter() {System.out.println("You inserted a quarter");gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getHasQuarterState());}public void ejectQuarter() {System.out.println("You haven't inserted a quarter");}public void turnCrank() {System.out.println("You turned, but there's no quarter");}public void dispense() {System.out.println("You need to pay first");} public String toString() {return "waiting for quarter";}
}
- 售罄状态
public class SoldOutState implements State {GumballMachine gumballMachine;public SoldOutState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;}public void insertQuarter() {System.out.println("You can't insert a quarter, the machine is sold out");}public void ejectQuarter() {System.out.println("You can't eject, you haven't inserted a quarter yet");}public void turnCrank() {System.out.println("You turned, but there are no gumballs");}public void dispense() {System.out.println("No gumball dispensed");}public String toString() {return "sold out";}
}
- 售卖(出)状态
public class SoldState implements State {GumballMachine gumballMachine;public SoldState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;}public void insertQuarter() {System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a gumball");}public void ejectQuarter() {System.out.println("Sorry, you already turned the crank");}public void turnCrank() {System.out.println("Turning twice doesn't get you another gumball!");}public void dispense() {gumballMachine.releaseBall();if (gumballMachine.getCount() > 0) {gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());} else {System.out.println("Oops, out of gumballs!");gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());}}public String toString() {return "dispensing a gumball";}
}
- Winner 状态:出两糖状态
public class WinnerState implements State {GumballMachine gumballMachine;public WinnerState(GumballMachine gumballMachine) {this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine;}public void insertQuarter() {System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a Gumball");}public void ejectQuarter() {System.out.println("Please wait, we're already giving you a Gumball");}public void turnCrank() {System.out.println("Turning again doesn't get you another gumball!");}public void dispense() {System.out.println("YOU'RE A WINNER! You get two gumballs for your quarter");gumballMachine.releaseBall();if (gumballMachine.getCount() == 0) {gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());} else {gumballMachine.releaseBall();if (gumballMachine.getCount() > 0) {gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getNoQuarterState());} else {System.out.println("Oops, out of gumballs!");gumballMachine.setState(gumballMachine.getSoldOutState());}}}public String toString() {return "despensing two gumballs for your quarter, because YOU'RE A WINNER!";}
}2.6 状态模式实例:自行车升降档
可以将自身作为参数传递给处理该请求的状态对象,以允许状态对象在必要时访问上下文
状态转换交给 State
- 自行车:即 Context
public class Bike {private GearState gearState;public Bike(GearState gearState) {this.gearState = gearState;}public GearState getGearState() {return gearState;}public void setGearState(GearState gearState) {this.gearState = gearState;}public void gearUp() {gearState.gearUp(this);}public void gearDown() {gearState.gearDown(this);}
}- 档数状态:抽象状态
/*** 档数状态*/
public abstract class GearState {public GearState() {}// 升档public abstract void gearUp(Bike bike);// 降档public abstract void gearDown(Bike bike);
}
- 档数状态:实现类
public class FirstGearState extends GearState {@Overridepublic void gearUp(Bike bike) {System.out.print("Moving Up from FirstGear to SecondGear!\t");bike.setGearState(new SecondGearState());System.out.println("Current GearState: " + bike.getGearState().toString());}@Overridepublic void gearDown(Bike bike) {System.out.print("Already in the FirstGear - cannot go lower!\t");System.out.println("Current GearState: " + bike.getGearState().toString());}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "First Gear";}
}public class SecondGearState extends GearState {@Overridepublic void gearUp(Bike bike) {System.out.print("Moving Up from SecondGear to ThirdGear!\t");bike.setGearState(new ThirdGearState());System.out.println("Current GearState: " + bike.getGearState().toString());}@Overridepublic void gearDown(Bike bike) {System.out.print("Moving Down from SecondGear to FirstGear!\t");bike.setGearState(new FirstGearState());System.out.println("Current GearState: " + bike.getGearState().toString());}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Second Gear";}
}public class ThirdGearState extends GearState {@Overridepublic void gearUp(Bike bike) {System.out.print("Already in the ThirdGear - cannot go higher!\t");System.out.println("Current GearState: " + bike.getGearState().toString());}@Overridepublic void gearDown(Bike bike) {System.out.println("Moving Down from ThirdGear to SecondGear!\t");bike.setGearState(new SecondGearState());System.out.println("Current GearState: " + bike.getGearState().toString());}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Third Gear";}
}- Client 测试
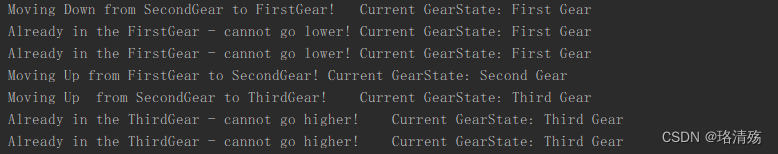
public class StateClientDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Bike bike = new Bike(new SecondGearState());bike.gearDown();bike.gearDown();bike.gearDown();bike.gearUp();bike.gearUp();bike.gearUp();bike.gearUp();}
}